| Korean Alphabet | 한글 Hangul |
|---|---|
| Script | Featural alphabet |
| Type | / |
| Creator | Sejong of Joseon |
| Time period | 1443-Presennt |
| Direction | Wikipedia |
| Print basis | writing direction (different variantts of Hangul) |
| Languages | Korean, Jeju, Cia-Cia, Taiwanese |
| Official script of | South Korea, North Korea |
| Unicode alias | Hangul |
| Unicode range | U+AC00–U+D7AF U+1100–U+11FF U+3130–U+318F U+A960–U+A97F U+D7B0–U+D7FF |
| Unicode alias | Hangul |
|---|---|
| Unicode range | U+AC00–U+D7AF |
| Unicode range | U+1100–U+11FF |
| Unicode range | U+3130–U+318F |
| Unicode range | U+A960–U+A97F |
| Unicode range | U+D7B0–U+D7FF |

The Korean alphabet, known as Hangul (Hangeul)[note 1] in South Korea
and Chosŏn'gŭl in North Korea, is a writing system for the Korean
language created by King Sejong the Great in 1443.[2][3] The letters
for the five basic consonants reflect the shape of the speech organs
used to pronounce them, and they are systematically modified to
indicate phonetic features; similarly, the vowel letters are
systematically modified for related sounds, making Hangul a featural
writing system.
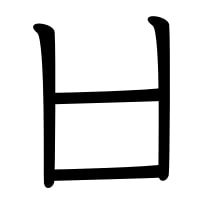
Modern Hangul orthography uses 24 basic letters: 14 consonant letters
(ㄱ ㄴ ㄷ ㄹ ㅁ ㅂ ㅅ ㅇ ㅈ ㅊ ㅋ ㅌ ㅍ ㅎ) and 10 vowel letters (ㅏ
ㅑ ㅓ ㅕ ㅗ ㅛ ㅜ ㅠ ㅡ ㅣ). There are also 27 complex letters formed
by combining the basic letters: 5 tense consonant letters (ㄲ ㄸ ㅃ ㅆ
ㅉ), 11 complex consonant letters (ㄳ ㄵ ㄶ ㄺ ㄻ ㄼ ㄽ ㄾ ㄿ ㅀ ㅄ)
and 11 complex vowel letters (ㅐ ㅒ ㅔ ㅖ ㅘ ㅙ ㅚ ㅝ ㅞ ㅟ ㅢ). Four
basic letters in the original alphabet are no longer used: 1 vowel
letter (ㆍ) and 3 consonant letters (ㅿ ㆁ ㆆ)
The Korean letters are written in syllabic blocks with the alphabetic
letters arranged in two dimensions. For example, Hangeul in Korean is
spelled 한글, not ㅎㅏㄴㄱㅡㄹ. These syllables begin with a consonant
letter, then a vowel letter, and then potentially another consonant
letter. If the syllable begins with a vowel sound, then the consonant
"ㅇ" will act as a silent placeholder. Syllables may begin with basic
or tense consonants, but not complex ones. The vowel can be basic or
complex, while the second consonant can be basic, complex or a limited
number of tense consonants. The way the syllable is structured depends
on if the vowel is a "tall" vowel (vertical base line) or a "fat"
vowel (horizontal base line); if the vowel is "tall" then the first
consonant and vowel are written above the second consonant (if there
is one), whereas if a vowel is "fat" then all of the components are
written individually top to bottom.
As it combines the features of alphabetic and syllabic writing
systems, it has been described as an "alphabetic syllabary". As
in traditional Chinese and Japanese writing, Korean texts were
traditionally written top to bottom, right to left, and are
occasionally still written this way for stylistic purposes. Today, it
is typically written from left to right with spaces between words and
western-style punctuation. It is the official writing system of
Korea, including both North and South Korea. It is a co-official
writing system in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture and
Changbai Korean Autonomous County in Jilin Province, China. It is also
sometimes used to write the Cia-Cia language spoken near the town of
Baubau, Indonesia. The Taiwanese linguist Hsu Tsao-te [zh] developed
and used a modified Hangul alphabet to represent spoken Taiwanese
Hokkien and was later supported by Ang Ui-jin (see Taiwanese
Hangul).